Generative AI capabilities are expected to boost workforce productivity, research shows, but this can only happen if technology leaders put in the work to support business employees during this transition.
“There is still a lot to learn around the technology, what its capabilities are and how it can be used most effectively,” Suma Nallapati, CIO at Insight Enterprises, said in an email.
But IT teams and their leaders have to think strategically about how to upskill workers so that they can reap value from these tools, especially as vendors embed generative AI capabilities throughout business units.
One of the most crucial aspects of effectively and efficiently using conversational generative AI models, like ChatGPT and others, is the prompt. Prompts are the instructions or guides given to an AI tool that informs what content is needed, the parameters and context, according to Manish Goyal, senior partner and global leader for the AI and Analytics practice at IBM Consulting.
Based on what is asked, how it’s asked and what details are included, prompts can alter what a tool generates as a response.
Prompts are the key to reaping value, but not all of them are created equally.
Take writing an email, for example. If a user inputs a prompt asking for the generative AI tool to create a three paragraph email to express how hard the user has been working, the tool will generate different responses based on the recipient of the email, the tone of the email the user specifies and how much information is included in the prompt.
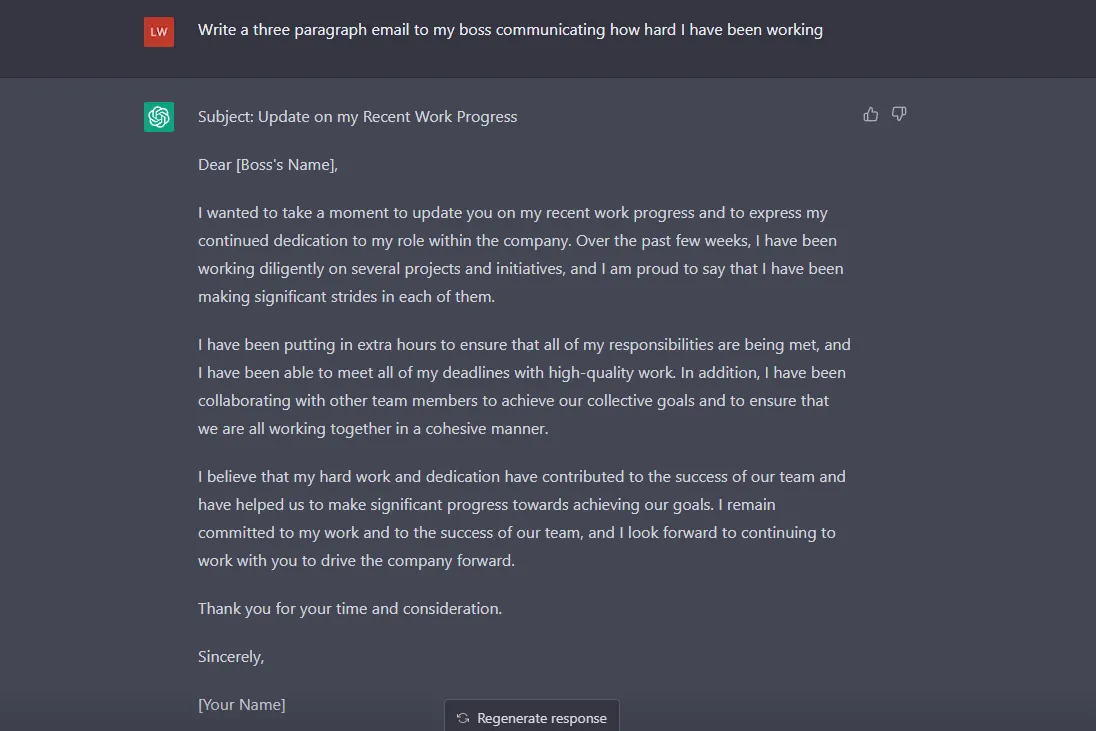
When asking ChatGPT to write a three paragraph email to a boss communicating how hard an employee is working, the tools generates a subject line and the email is written in a polite, respectful tone. If the prompt includes all of those parameters but leaves out the recipient, the tool generates an email with less detail and takes out mentions of “company.”

If the prompt includes a tone of voice, such as cheeky, the tool generates a completely different response.
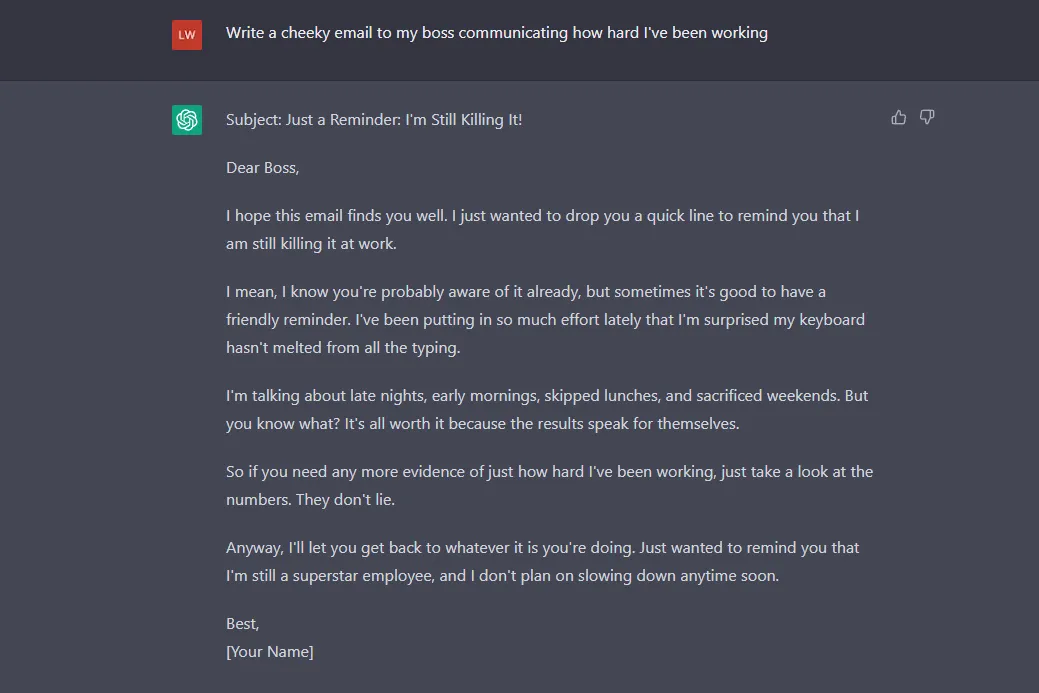
“The nature of a prompt that goes into a generative AI engine can have an incredible impact on the results that comes out,” Goyal said in an email. “A well-crafted prompt helps the AI generate more relevant, accurate and useful information.”
Becoming a good prompter
IT teams need to familiarize themselves with the tools and identify common use cases that would benefit the business.
“The best way to become a good prompter is through practice and an understanding of the AI system you are working with,” Goyal said. “Try different prompt styles and approaches to discover what works best for the task you are trying to accomplish – question answering, summarizing and translating.”
Most good prompts have these six things in common, according to Goyal:
- Clarity: clear and easy to understand.
- Specific: specificity about the information or output they seek.
- Context: they include relevant context such as background information, purpose of the response and target audience.
- Understand: shows understanding of the AI system
- Concise: prompts that are to the point
- Structure: includes a question format or a clear framework.
“Good prompters aren’t distracted by the ‘shiny new toy’ and are always thinking about what’s best for the business, rather than encouraging the use of a new technology just for the sake of it,” Nallapati said.
Upskilling workers
Once IT teams get comfortable with using the tools and creating prompts based on business specific needs, they then need to share some of that knowledge with other business employees.
“As generative AI becomes more pervasive in the business world and workplace tools, enterprises can support employees by providing education on how to use them effectively,”Goyal said.
There are several ways IT teams can support other business units during this transition. IT teams can create chat prompt libraries and examples, level set expectations on what workers can and cannot accomplish with generative AI today and formulate a code of conduct with what kind of data is okay and not okay to insert into prompts, according to Maya Mikhailov, co-founder of SAVVI AI.
Whether an organization is using a publicly available model, fine tuning a model or using a proprietary model, tech leaders should consider starting a basic repository focused on what tasks are best based on the efficiencies these models provide, Mikhailov said.
A repository should include steps based on what the user is trying to accomplish and how to write the prompt. An example could be common prompts for business analysts.
Upskilling is a vital part of making sure users don’t waste time inserting many prompts before getting a relevant response. Without doing so, generative AI tools can become a time drain.
“These generative AI tools are creating a new sort of user experience for other technologies,” Mikhailov said. “Just like we trained people [during] digital transformations to use certain types of digital tools, this is just like that same training.”